What Are Plug Valves and How Do They Work?
Plug valves are essential components in fluid control systems. They offer a simple yet effective way to manage flow. Characterized by a cylindrical plug that rotates, these valves can easily open or close. They are popular in various industries due to their reliability and moderate cost.
Understanding how plug valves function can lead to optimized processes. Their design allows for minimal restrictions on flow. However, choosing the right valve can be challenging. There are different sizes and materials to consider. Sometimes, users overlook the importance of maintenance. Regular checks can prevent unexpected failures.
Plug valves have both advantages and limitations. They work well in on/off applications but may not perform optimally in throttling situations. Balancing these factors can be a puzzle. Yet, knowing their role in a system enhances overall efficiency. Investing time in learning about plug valves pays off in the long run.

What is a Plug Valve? Definition and Overview
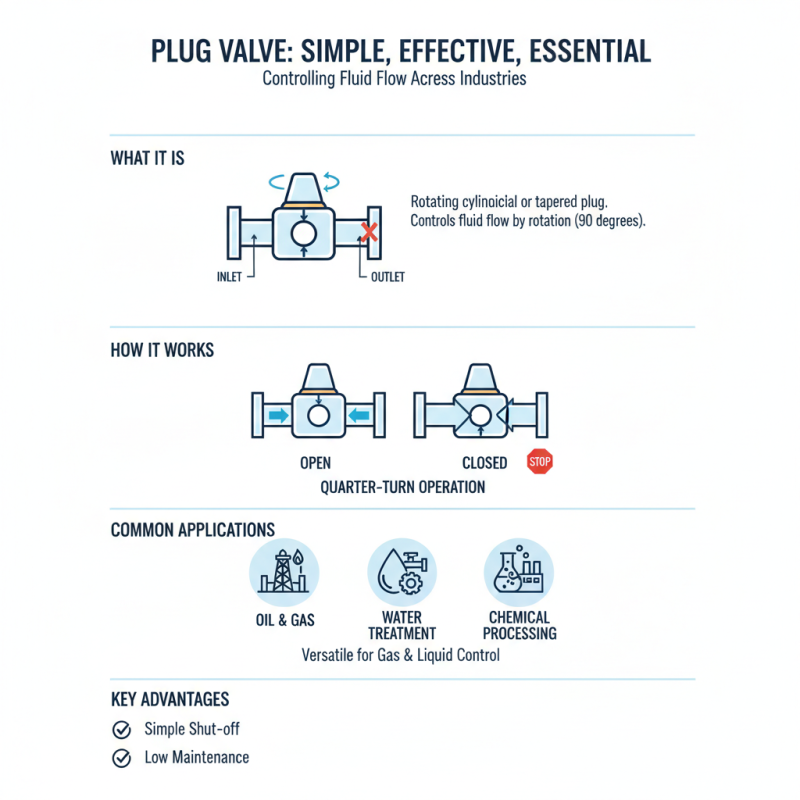
A plug valve is a simple yet effective device used in various industrial applications. It features a cylindrical or tapered plug that rotates to control fluid flow. Typically, these valves are employed in pipelines for gas and liquid control. They are particularly valuable in industries like oil and gas, water treatment, and chemical processing.
Plug valves can be spherical, tapered, or cylindrical in design. According to a recent report by Global Market Insights, the global plug valve market is projected to reach USD 1.2 billion by 2025. This reflects a growing need for efficient flow control solutions. However, their design can pose challenges. A common issue is the accumulation of debris around the plug. This can hinder the smooth operation of the valve, causing leaks or complete failure.
Moreover, maintenance for plug valves can be overlooked. Regular inspections are crucial to ensure they function properly. The absence of this can lead to operational downtime. In an era of increasing pressure for reliability, it's essential to address these gaps. Companies must acknowledge that without proper care, even simple devices like plug valves can become liabilities instead of assets.
Types of Plug Valves: A Comparative Analysis of Designs
Plug valves are essential components in various industrial applications. Their design allows for easy control of fluid flow. When it comes to types of plug valves, several options exist. Each has unique features that serve different purposes.
The most common design is the cylindrical plug. It offers straightforward on/off functionality. However, its sealing capability can be limited in high-pressure systems. Another design is the tapered plug. This type has a conical shape that enhances sealing, making it suitable for more demanding environments. Yet, it can be challenging to operate due to its fit within the valve body.
Lastly, there are four-way plug valves. These enable flow direction changes, providing versatility. They can be complex and may require more maintenance. Choosing the right valve design often involves trade-offs. Assessing flow requirements and pressure levels is essential. Sometimes, a valve might not perform as expected. Understanding these design differences can lead to better application choices.
Types of Plug Valves and Their Applications
This bar chart illustrates the various types of plug valves and their common applications in industrial settings. Each type of valve is represented by the number of applications it is typically used for, highlighting the versatility and functionality of different designs.
Principle of Operation: How Plug Valves Control Flow
Plug valves are essential components in various fluid control systems. They operate by rotating a cylindrical plug within the valve body to regulate flow. This design allows for quick opening and closing, often requiring only a quarter turn. According to industry reports, plug valves can achieve up to 95% flow efficiency, making them ideal for applications where minimal pressure drop is critical.
The principle of operation is straightforward. As the plug aligns with the flow path, fluid moves freely. When rotated, the plug obstructs the flow, creating a seamless transition between open and closed states. Many industries rely on this swift action, particularly in gas and oil, where response time can make a difference.
**Tip:** Regular maintenance checks can prevent potential leaks. A worn plug may not seal properly, leading to inefficiency.
It's essential to understand that plug valves may have limitations. They can struggle with highly viscous fluids, which might impede their movement. Evaluating system requirements is key. **Tip:** Consider the fluid's characteristics before selecting a valve type. Failure to do so could lead to costly downtime or performance issues.
What Are Plug Valves and How Do They Work?
| Feature | Description | Applications | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Rotary valve with a cylindrical or tapered plug | Water, oil, gas pipelines | Tight sealing, minimal flow resistance | Can be difficult to repair |
| Operation | Rotate the plug to start or stop flow | Chemical processing | Durable under high pressure | Limited throttling capability |
| Materials | Brass, stainless steel, plastic | Water treatment plants | Versatile in various environments | Potential for material degradation |
| Sizes | Varies from small to large dimensions | Industrial fluid transport | Customizable to system requirements | Cost may increase with size |
Applications of Plug Valves in Various Industries
Plug valves are essential in various sectors, including oil and gas, water treatment, and food production. In the oil and gas industry, they control the flow of hydrocarbons. Their design ensures minimal leakage and can function under high pressure. However, some users report difficulties with maintenance, especially in extreme conditions.
In water treatment, plug valves help regulate water flow effectively. Their simplicity allows for easy operation, but sometimes they fail to provide precise flow control needed for certain applications. The food industry utilizes these valves for their sanitary design. The ability to clean them thoroughly is crucial, but this can lead to potential complications if not done properly.
Overall, industries rely on plug valves for efficiency and reliability. Yet, the challenges in maintenance and control call for continuous evaluation and improvement. The balance between performance and simplicity remains an area of focus. Each sector must assess the specific needs and applications of plug valves closely.
Key Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Plug Valves
Plug valves are essential components in many industrial applications. They primarily control flow by utilizing a rotating plug. Understanding their advantages and disadvantages is vital for efficient operation.
One key advantage of plug valves is their simplicity. They have fewer components, which makes them easier to manufacture. They are also durable and can handle various temperatures and pressures. However, their design can lead to some issues. They may not provide a perfect seal, especially over time. This can result in leaks if not maintained properly.
Tips: Regular maintenance is crucial. Inspect for wear and tear, especially if used in high-pressure systems. Additionally, consider the application. Plug valves work well for on/off operations but may fall short in throttling applications.
Another downside is the potential for sticking. If not operated frequently, the plug might seize. Additionally, the torque required to turn the plug can be significant, making them less suitable for automated systems.
Tips: Use lubricants to minimize wear. This can help ensure the valve operates smoothly. Be sure to choose the right size and type for your specific needs. Proper sizing can prevent many problems down the line.
Related Posts
-

Understanding the Importance of Gate Valves in Modern Energy Infrastructure
-

Common Issues Faced by Gate Valves in High Pressure Applications
-
Top 10 Benefits of Triple Offset Butterfly Valves for Your Projects?
-

Understanding the Varieties of Cast Iron Butterfly Valves in Industrial Applications
-

Unlocking Performance with Best Stainless Steel Valves Comprehensive Technical Parameters and How to Choose the Right Fit
-

Emerging Trends in Butterfly Valves Industry Exhibited at China Import and Export Fair 2025
